Publications
A complete up-to-date list of publications of Robert can be found on Google Scholar and full-texts might be available from the Warwick Research Active Portal (WRAP).
Circadian effects on stroke outcome – Did we not wake up in time for neuroprotection?
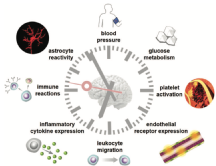 |
The occurrence of stroke in humans peaks in the morning. A recent study revealed that time of day mitigates the therapeutic impact of neuroprotective paradigms. These findings might not only explain the previous failure of trans- lation of neuroprotective therapies but inspire new paradigms in stroke chronopathophysiology research. Taking chro- notype into account may complement the many factors that influence efficacy of experimental therapies in stroke. |
Dose and time-dependent tolerability and efficacy of organo-osmium complex FY26 and its tissue pharmacokinetics in hepatocarcinoma-bearing mice
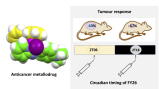 |
The organo-osmium complex [OsII(ɳ6-p-cym)(PhAzPy-NMe2)I]+ (FY26) exhibits promising in vitro antitumour activity against mouse hepatocarcinoma Hepa1-6 and other mouse or human cancer cell lines. Here, we drastically enhance water solubility of FY26 through the replacement of the PF6-counter-anion with chloride using a novel synthesis method. FY26.PF6 and FY26.Cl displayed similar in vitro cytoxicity in two cancer cell models. We then show the moderate and late anticancer efficacy of FY26.PF6 and FY26.Cl in a subcutaneous murine hepatocarcinoma mouse model. Both efficacy and tolerability varied according to FY26 circadian dosing time in hepatocarcinoma tumour-bearing mice. Tumour and liver uptake of the drug were determined over 48 h following FY26.Cl administration at Zeitgeber 6 (ZT6), when the drug is least toxic (in the middle of the light span when mice are resting). Our studies suggest the need to administer protracted low doses of FY26 at ZT6 in order to optimize its delivery schedule, for example through the use of chrono-releasing nanoparticles. |
Low-Cost Microfabrication Tool Box
Microsystems are key enabling technologies, with applications found in almost every industrial field, including in vitro diagnostic, energy harvesting, automotive, telecommunication, drug screening. Yet, their development for commercial or educational purposes has typically been limited to specialized laboratories in upper-income countries. In this paper, we describe a range of low-cost approaches and equipment (below £1000), which will enable researchers to build a low-cost toolbox.
