capabilities
The Advanced Bioimaging RTP specializes in imaging of biological specimens at high resolution. We have several options available and would be happy to discuss your requirements. A brief (but not exhaustive) overview is given below.
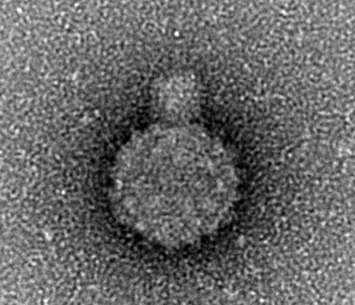
Negative Stain TEM
Negative staining is routinely used to image smaller biological samples such as viruses and protein complexes. The heavy metal stain envelops the organic material, resulting in an outline of its shape. This is a quick and easy method to look at homogeneity and morphology of samples. We usually use the JEOL 2011 for negatively stained samples. |
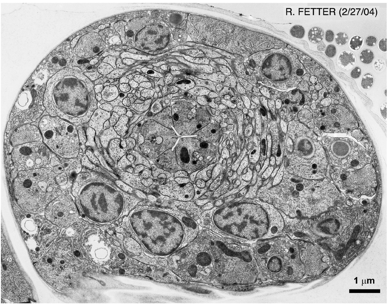
Resin section TEM
Resin sectioning is a useful way to look at cells or tissues. It offers a high resolution but small field of view compared to light microscopy. . |
|
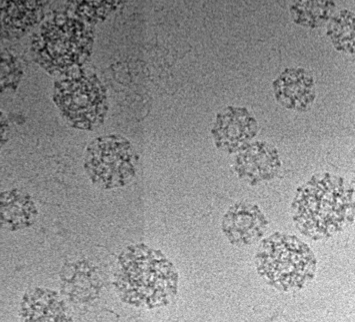
Cryo-TEM
Transmission electron microscopy of vitreous frozen samples allows for high-resolution imaging that shows the interior structure as well as the envelope of the samples. This can be done on either the JEOL 2011 to investigate morphology, or the JEOL 2200FS with direct electron detector for high-resolution 3D reconstructions of the protein structure. |
|
Cryo-electron tomography
Electron tomography allows for 3D reconstruction of macromolecular structures in their cellular context. |
Light sheet microscopyLight sheet microscopy is a method that allows for fluorescent imaging of relatively large and living specimens with low phototoxicity. Because the sample gets imaged from two orthogonal angles, the data has good resolution in three dimensions. |
Thin sectioningOur brand-new cryo-ultramicrotome is set up for use at room temperature or cooled with liquid nitrogen. It can be used for CEMOVIS, Tokuyasu and sectioning of resin-embedded samples. |