Identified: A mechanism that protects plant fertility from stress
· Spikes in temperature can affect a plant’s fertility, resulting in a reduction of yield and economic loss
· How plants can protect themselves from stress has been studied by a consortium led by the University of Warwick
· Two argonaute-like proteins protect the plant’s fertility, understanding these proteins is critical to safeguarding crop production
As Temperatures rise due to global warming the need to protect plants from stressful conditions has increased, as stress can cause a loss in yield and cause further impact economically. A consortium led by the University of Warwick have successfully identified two proteins that protect crops from stress, which is key in safeguarding food production.
Plant fertility is dramatically affected by spikes in temperature, directly resulting in yield reduction and economic loss. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underpin plant fertility under environmental constraints is critical to safeguarding food production.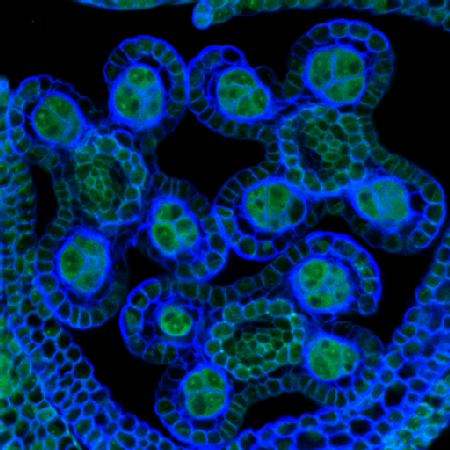
In the paper, ‘A transposon surveillance mechanism that safeguards plant male fertility during stress’, published in the journal Nature Plants, led by researchers from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick have studied the molecular mechanisms that maize plants utilise to safeguard fertility under high temperatures, and identified two Argonaute-like (AGO) proteins that protect the male sex cells.
By subjecting maize plants with non-functional AGO proteins to different growth conditions, researchers discovered that a 5°C increase in ambient temperature dramatically decreased male fertility.
Using a multidisciplinary approach, the team found that higher temperatures activated small pieces of ribonucleic acid (or small RNAs) in wild-type plants, which bind to these AGO proteins to control the activity of stress-activated jumping genes - pieces of DNA that can copy themselves into different parts of the genome. Therefore, these AGO proteins control the activity of jumping-genes, thereby protect plant fertility.
Professor Jose Gutierrez-Marcos, from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick explains:
“We have essentially found that when plants are stressed by high temperatures they activate an RNA-guided surveillance mechanism in the form of small RNAs and Argonaute proteins, in reproductive cells which are critical to sustain male fertility and ultimately plant survival.
“Understanding the molecular mechanism implicated in safeguarding plant fertility is critical to safeguard future crop production under unpredictable and stressful climatic conditions.”
Dr Charo del Genio, from the School of Computing, Electronics and Mathematics at Coventry University adds:
"Modelling the structure of the Argonaute proteins and simulating them at the level of the single atoms revealed how they change their electric charge when subject to thermal stress, initiating the process that brings the jumping genes back under control."
ENDS
1 MARCH 2021
NOTES TO EDITORS
This research was funded by the BBSRC and conducted in collaboration with Coventry University, University of Wyoming, University of Missouri, Gregor Mendel Institute, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and Biogemma-Limagrain.
High-res images available at:
https://warwick.ac.uk/services/communications/medialibrary/images/february_2021/jose_image.png
Caption: Argonaute-like (AGO) proteins in male germline precursor cells
Credit: University of Warwick
Paper available to view at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41477-020-00818-5#:~:text=Our%20results%20demonstrate%20that%20an,transposons%20in%20male%20germ%20cells.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION PLEASE CONTACT:
Alice Scott
Media Relations Manager – Science
University of Warwick
Tel: +44 (0) 7920 531 221
E-mail: alice.j.scott@warwick.ac.uk
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION PLEASE CONTACT:
Alice Scott
Media Relations Manager – Science
University of Warwick
Tel: +44 (0) 7920 531 221
E-mail: alice.j.scott@warwick.ac.uk
