Thermal analysis
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is the quantitative measurement of phase transitions and is used to determine transition temperatures and phase compositions, for example glass transitions in polymers, glass/crystal fractions, and purity determination in pharmaceuticals. High temperature phase changes such as those in metals or ceramics can be monitored.
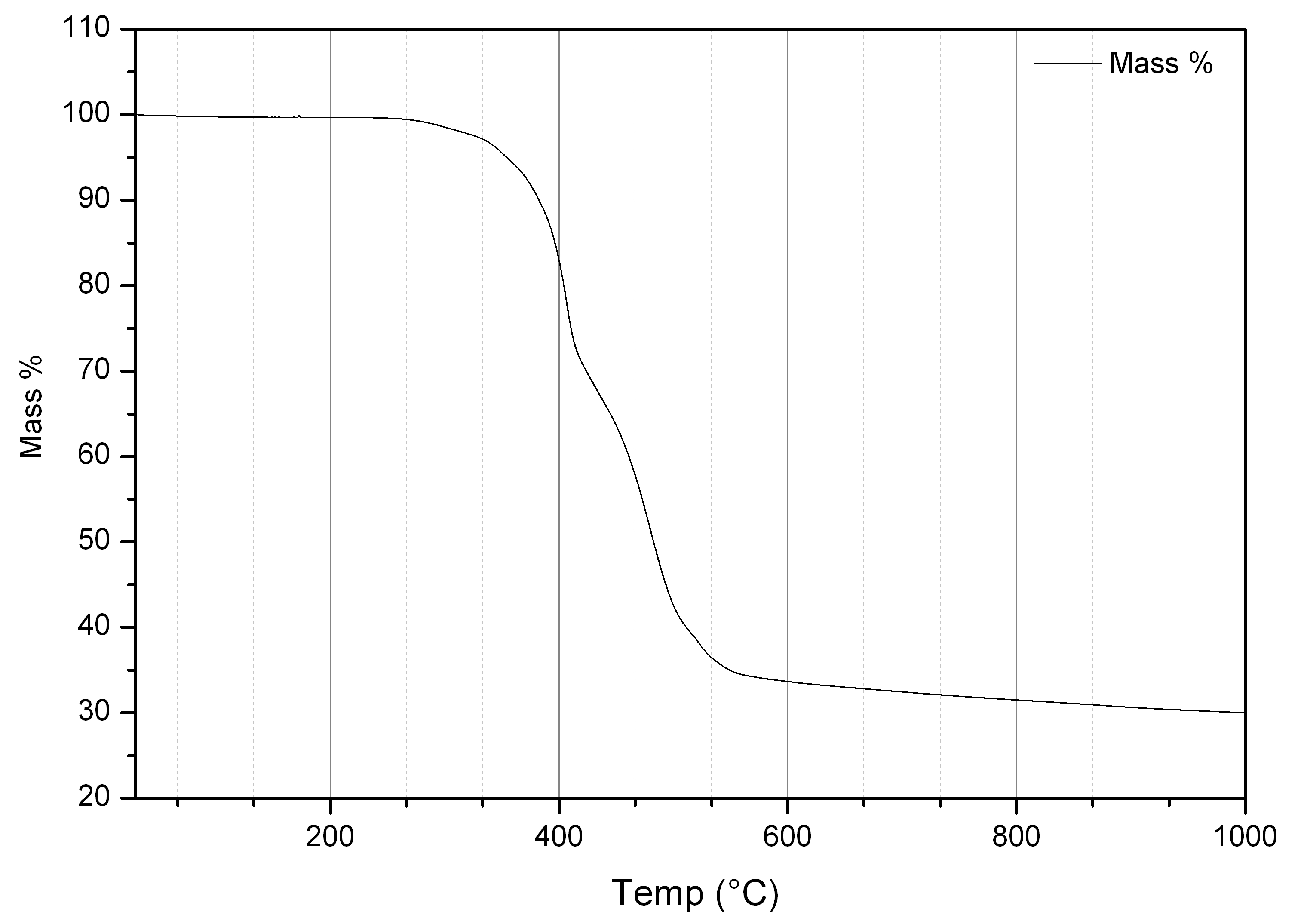
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) can be used to determine the thermodynamics and kinetics of processes involving mass loss such as corrosion and oxidation, or to monitor dehydration or thermal stability of samples.
How does it work?
In differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) the difference in heat flow between a sample and a reference material are measured with temperature or time. The sample absorbs or releases heat during processes such as melting or glass transitions, and the energies of these processes can be determined.In thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), the mass of a sample is constantly monitored during heating. A profile of mass with temperature or time can show processes such as dehydration or decomposition.
Applications:
Liquid crystals; oxidative stability; safety screening; drug analysis; general chemical analysis; food science; polymers; metals.
Sample Handling Requirements:
Solids.
Complementary Techniques:
Warwick capability:
Mettler Toledo DSC1-400, DSC1-STAR, DSC1-1600.

Contact:
Claire Gerard: / 07385 145064
