X-Ray Source
|
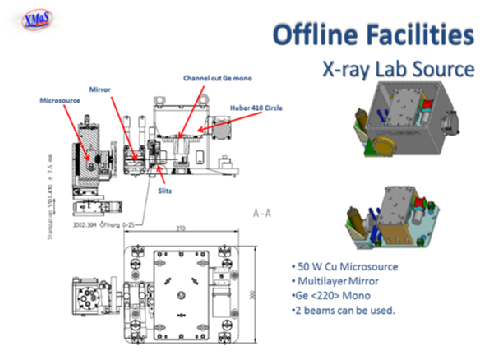
The laboratory x-ray source, situated at the end of the XMaS beamline, is based on a copper micro-focus tube (Vari Aqua 0.080NWCMF24 Petrick GmbH, Germany). The electron beam spot size at the water cooled anode is approximately 50 μm, with an electron beam energy of 40 keV. An INEL XRC60 power supply is used to power the tube, which contains electronics to drive the x-ray shutter, that is mounted within the tube. The power supply also houses the onboard water cooling system to dissipate the heat generated at the anode. The power supply and shutter can be controlled remotely by using a Linux terminal when all of the appropriate interlocks are in place. All of the safety interlocks are based on the ESRF personal safety system (PSS) and the appropriate online safety training must have been followed to use the source. The operating system of the offline x-ray source is based on the SPEC control systemLink opens in a new window, as used on the main beamline. |
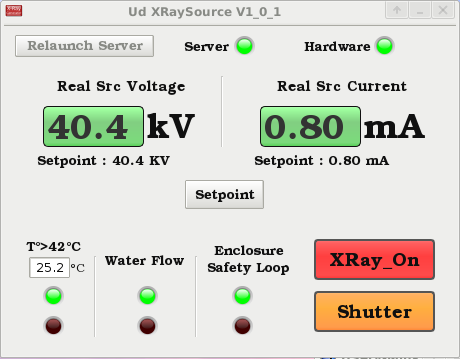 Window used to control the x-ray tube and shutter on the XMaS laboratory source. Window used to control the x-ray tube and shutter on the XMaS laboratory source. |
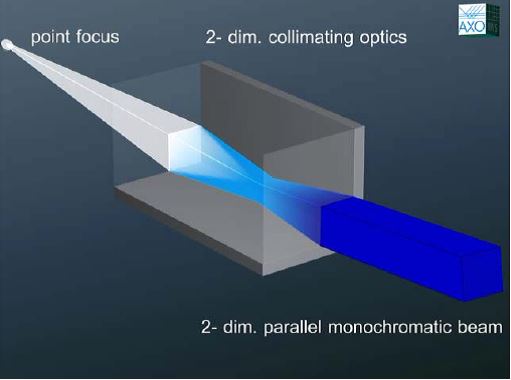
The Collimating MirrorThe x-rays from the tube are collimated using an ASTIX-c 2-dimension parallel beam multilayer mirror optics. The mirror acts as a “band pass filter”, accepting only the radiation around the copper Kα1 and Kα2 lines and the copper Kβ radiation is rejected. A full description of the mirror optics can be found in the paper by Montel [1]. By only using the mirror as a monochromator and focussing device, we have a reasonably high flux, but a low resolution, making this configuration good for such techniques as SAXS.
|
|
Schematic of the mirror geometry.
The Germanium <220> Channel Cut Monochromator
For high resolution experiments, there is the option to insert a germanium <220> channel cut monochromator into the beam. This allows to separate out the copper Kα1 and Kα2 lines and have a more monochromatic beam. However, intensity is reduced by approximately a factor of 20. For normal use, the germanium monochromator is tuned to the stronger Kα1 line.
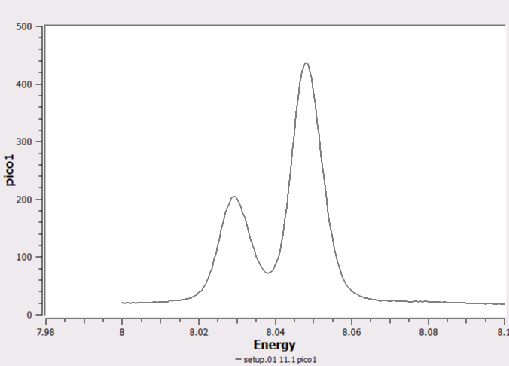
Separation of the copper Kα2 and Kα1 lines using the germanium monochromator.
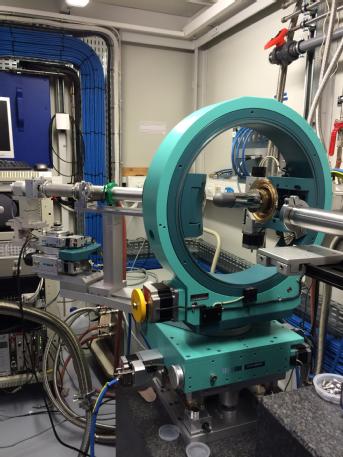
The DiffractometerA Huber 4-circle diffractometer is available for sample mounting. This instrument has a nearly identical Eulerian cradle as the main instrument on the synchrotron beamline and most of the sample environments available on the XMaS beamline are also compatible with the offline x-ray source. Reference[1] M. Montel - "The X-Ray Microscope with Catamegonic Roof-Shaped Objective" in: X-ray Microscopy and Microradiography, Vol.5, 1957, pp 177 - 185 |
 |