Departmental news
New paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) Journal
Andrew Jackson (Warwick), Theodoros Kapourniotis (STFC) and Animesh Datta (Warwick) have published their paper ‘Accreditation of Analogue Quantum Simulators’ in the PNAS journal.
Life Sciences Research with Impact
The recently published BBSRC Impact Showcase 2023 presents a collection of impact stories arising from BBSRC investments. The showcase highlights the vital role bioscience has in addressing key strategic global challenges and features research by Professor Eric Holub to develop new varieties of beans compatible with the British Climate.
Find out more (Scroll down the homepage to find 'Homegrown production of designer dry beans').
New paper published in Nature Physics
Dr Wei Peng, lead author with colleagues Professor Ana Sanchez, Professor David Walker and Steven Hindmarsh have worked collaboratively with other institutions to publish their paper titled Flexoelectric polarizing and control of a ferromagnetic metalLink opens in a new window in Nature Physics on Jan. 17, 2024.
Securing the future of offshore infrastructure - major training grant for Warwick Academic
Professor Xueyu Geng secures funding as part of a major EU consortium.
Professor Alok Choudhary: Impact of the Red Sea crisis on global supply chains
 Expert comment from Professor of Supply Chain Management, Alok Choudhary.
Expert comment from Professor of Supply Chain Management, Alok Choudhary.
“The ongoing Red Sea crisis might have far-reaching consequences on the global supply chain, trade, and economic dynamics. Serving as the shortest sea route connecting Asia and Europe, the Suez Canal transports 17,000 ships annually, representing 12% of the world's total trade volume and $1 trillion worth of goods.
“The implications of this disruption on trade are significant. Rerouting ships an additional 3500 nautical miles is expected to result in significant delays, causing logistical challenges for major companies. The increased shipping and logistics costs incurred due to longer travel times are likely to be passed on to consumers, leading to a potential spike in prices for a wide array of goods, from everyday consumer items, oil and gas to crucial components for industries such as automotive and manufacturing.
“The ripple effect on production cycles is a cause for concern, as delays in delivering key components may lead to further disruptions. In particular, the automotive and consumer goods industries may face challenges in maintaining production schedules if crucial components do not reach their destinations on time.
“One of the most immediate impacts could be felt in the oil market, with potential consequences for global oil prices. The disruption in the timely transportation of both refined and crude oil through the canal may contribute to an increase in oil prices. This could have a cascading effect on economies, particularly in regions heavily reliant on oil imports, and may be reflected at fuel pumps worldwide.
“Here in the UK, the rise in oil prices could pose a challenge to economic stability and may halt falling inflation. Higher shipping and logistics costs, coupled with potential delays in the delivery of goods, might contribute to inflationary pressures. This could have broader implications for the UK economy, impacting consumer spending and overall economic growth.”
Read more about Supply Chain research at WMG here: https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/sci/wmg/research/research-areas/supply-chain
Metamaterials for Biomedical Imaging – EU research grant for Warwick Academics
Prof. Dave Hutchins and Prof. Peter Thomas have been awarded a grant of £260k as part of an MSCA Doctoral Network (“MetacMed”) under the Horizon Europe programme.
Warwick Agri-Tech ploughs the future of farming and forestry with robotics
 The University of Warwick announces Warwick Agri-Tech to help the future of farming with automation – addressing issues such as labour shortages, food insecurity and loss of biodiversity.
The University of Warwick announces Warwick Agri-Tech to help the future of farming with automation – addressing issues such as labour shortages, food insecurity and loss of biodiversity.
Warwick Agri-Tech, will also support the UK to meet climate targets while enabling the production of enough nutritious food for the growing population. It will combine two world class faculties at WMG at The University of Warwick and the School of Life Sciences (SLS), working with the High Value Manufacturing Catapult to spearhead automation in areas such as horticulture, crops and forestry.
Robots will be a key tool for farmers as food production comes under increasing pressure. There is a constant demand to grow enough high quality, nutritious food to feed an expanding human population, and to do so in a way that won’t harm the planet.
According to scientists, the UK will need to produce 50% more food by 2050, while reducing land consumption by 50%. This is further challenged by labour shortages, a broken food system and the fact we are overusing the Earth’s biocapacity (the capability of ecosystems to produce useful biological materials and to absorb waste).
The University of Warwick is in a unique position to tackle these issues and develop farming technology, with expertise in both automation and life science.
Warwick Agri-Tech was born out of an initial project which developed a crop monitoring robot (Crombot) to move autonomously up and down glasshouses and check fruit for ripeness. Officially launching today, with a visit from the Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA), Warwick Agri-Tech will continue its research on several key projects:
· An Autonomous Logistics Project – developing an autonomous vehicle to help horticultural companies to optimise their product handling logistics.
· A Smart Tree Production System – Warwick Agri-Tech is working with J&A Growers, who are the leading UK growers of quality bareroot trees and hedging, to autonomously sort and grade sapling trees. This will ensure resilience against labour shortages and is scalable in the face of the UK’s ambitious tree planting targets.
· Autonomous Precision Application – creating an autonomous, AI-based weed control robot, to reduce utilisation of herbicides by over 90% - improving soil health and biodiversity.
The University’s leading crop research centre at based at the Innovation Campus, Stratford-upon-Avon is a leading, 200-hectare agricultural research site. Scientists at the University will collaborate directly with industry partners and the Government to drive implementation of new technology in the farming sector.
Professor Gideon Henderson, Chief Scientific Adviser, said: “Seeing the innovation going on here is really inspiring – I firmly believe that Agri-Tech in the UK has a huge future and I look forward to seeing new ways of working being trialled here at Warwick become mainstream agricultural practices in the future.”
Professor David Greenwood, Director for Industrial Engagement, and CEO of the High Value Manufacturing Catapult at WMG, said: “The emerging needs of the agriculture sector have provided a perfect opportunity for The University of Warwick to bring together our expertise in manufacturing automation with our expertise in life sciences, so we can simultaneously develop robots suitable for use in greenhouses and fields, and ways of growing crops which take advantage of the opportunities of automation. As the UK struggles with availability of agricultural labour, and high food prices, this promises to unlock nutritious and affordable food for all.”
Professor Miriam Gifford, School of Life Sciences, University of Warwick, said: “Warwick Agri-Tech will benefit from the entrepreneurship of WMG and the history of excellence in agricultural innovation from the School of Life Sciences’ Warwick Crop Centre, plus the combined stakeholder groups to inform and enable outputs. The fresh food industries need automation urgently. Warwick Agri-Tech will grow rapidly into research and innovation space screaming for workable solutions and expecting substantial funding initiatives.”
More information about Warwick Agri-Tech here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vXC3jzqrga0
‘School Tasking’ Project enhances legal understanding for legally accountable 10-year-olds – research finds
Recent research by Dr Ali Struthers reveals 'School Tasking' widening participation project boosts children's legal comprehension, connecting them to cases influencing consumer rights, human rights, and broader justice and equality themes.
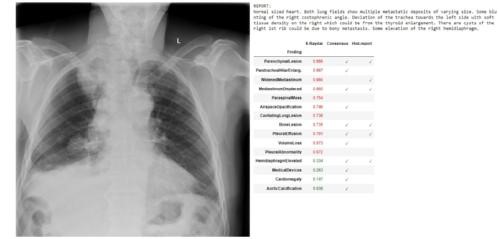
“The ultimate second opinion”: AI just as good as doctors at analysing X -rays, shows new study
AI can analyse X-rays and diagnose medical issues just as, or more, accurately than doctors, a new study led by the University of Warwick has found.
The AI, which has been trained on 2.8 million historic chest X-rays from over 1.5 million patients, scans X-Rays for 37 possible conditions.
It was just as accurate or more accurate than the doctor’s analysis at the time the X-ray was taken for 35 out of 37 conditions (94%).
The AI software can scan X-rays as soon as they are taken for possible conditions and flags any abnormalities. It will then give a percentage chance of each of the abnormalities being present. The AI also understands the seriousness of the different conditions and will flag the more urgent ones to doctors accordingly.
To verify the accuracy of the AI, a sample of over 1,400 X-Rays it had analysed were cross examined by a group of senior radiologists, who compared the diagnoses made by the AI with the historical diagnoses by radiologists at the time.
The AI is a collaboration between Warwick, King’s College London and several NHS sites funded by a Wellcome Trust Innovator Award. The programme also uses a large language model to understand the historical reports written by clinicians – the same underlying technology used by other AI programmes, such as ChatGPT.
Giovanni Montana, Professor of Data Science at WMG at the University of Warwick, and lead author, suggested that the AI tool could either be used as a screening tool for radiologists, or to offer “the ultimate second opinion”, avoiding human bias.
Professor Montana commented: “This programme has been trained on millions of X-rays and is highly accurate. It eliminates the elements of human error, which is unavoidable, and bias. If a patient is referred for an X-ray with a heart problem, doctors will inevitably focus on the heart over the lungs.
“This is totally understandable but runs the risk of undetected problems in other areas. This AI eliminates that human bias – it’s the ultimate second opinion”.
Co-author Professor Vicky Goh of King’s College London, and immediate past Chair of the Academic Committee at the Royal Society of Radiologists commented: “Current AI programmes available to us in the NHS only have a limited scope. Comprehensive AI programmes like this will be the future of medicine, with AI acting as a co-pilot for busy doctors.
 “With the acute shortage of radiologists in the UK, programmes like this will facilitate interpretation and reduce delays for diagnosis and treatment”.
“With the acute shortage of radiologists in the UK, programmes like this will facilitate interpretation and reduce delays for diagnosis and treatment”.
There is also the possibility that the AI could look at the X-Rays where no abnormalities are found, which is around half of all of them, and flag this to doctors in a way which could improve efficiency for the NHS. By allowing AI to weed out X-Rays with no abnormalities found, radiologists will have more time to focus on challenging and more critical tests.
A recent poll by the Royal College of Radiologists found that shortages of radiologists were leading to longer wait times, and delays in treatment, at 97% of the UK’s cancer treatment centres.
This AI software – entitled X-Raydar – is designed to help reduce the workload for doctors and cut delays. Remarkably, the research group has open sourced the entire software for non-commercial uses to speed up the pace of research development in this domain.
The software can be seen in use in a video here.
