Genotypes
The genotype of a plant is a word used describes the genetic make - up of the plant. The context that it is used depends upon whether it is being used to describe the whole genome, the DNA sequence of individual genes or a collection of scores at different genetic markers.
Traditionally a series of genetic markers are used to genotype individuals from a population. This information reveals the mosaic effect created by the inheritance of different portions of the parental chromosomes, created due to recombination between the parental chromosomes during meiosis. The image below highlights this patchwork of different genotypes at different genetic markers.
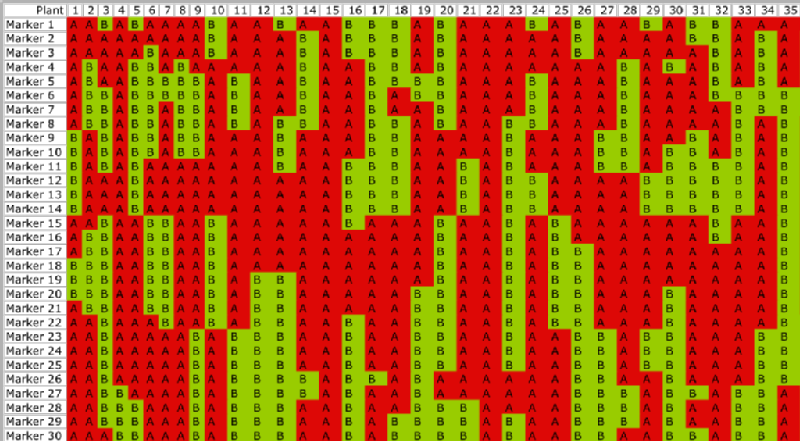
The 35 individuals from this population were scored using 30 SSR markers. The parental genotypes are: Female parent = A, Male parent = B.
When all the members of the population have been scored with the molecular markers, the data can be used to make a linkage map.
Since we can determine the genotype of individual lines at know positions in the genome, we can use the markers that flank desirable regions (e.g. QTLs) to select only those lines that contain the desirable genotype. This forms the basis for marker assisted selection (MAS).
