Nocturnal Hypoglycaemia detection via ECG & Artificial Intelligence in diabetic patients
| Project Title | Nocturnal Hypoglycaemia detection via ECG and Artificial Intelligence in Diabetic Patients |
| Dates | 01/06/2020 - 31/03/2022 |
| Funder | Wellcome Trust Translational Partnership |
| Project Lead | Prof. Leandro Pecchia |
Hypoglycaemia is a health condition that affects diabetes patients. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia range from confusion, moodiness, dizziness, feeling sweaty to coma and death in the most severe cases. Usually, in order to detect hypoglycaemia, several invasive finger prick tests are required. Therefore, the development of non-invasive methods for detecting hypoglycaemia has the potential to significantly improve the quality of life and disease management.
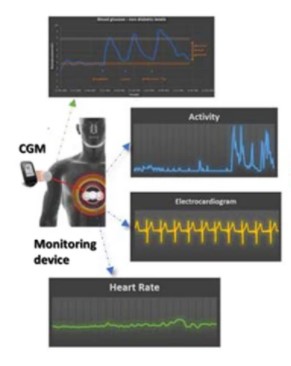
In the past 3 years, we developed an AI model able to detect hypoglycaemia via ECG in healthy subjects, without fingerpicks or needles.
In order to develop this technology, adult healthy subjects wore non-invasive sensors for continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) recording and Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) for continuous blood glucose measurements for two consecutive weeks while conducting their regular daily activities (paper at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-56927-5). The AI models detected nocturnal hypoglycaemic events achieving 87.5% sensitivity and 81.7% specificity in real-life scenarios.
The project ambition is to demonstrate that the AI model we developed can reliably detect nocturnal hypoglycaemia in Type I diabetic patients.
We expect to replicate the results obtained in healthy participants and increase the specificity/sensitivity of the AI models. Moreover, validating and testing our model on patients’ data will enable measuring the performance of our models with relevant clinical measures (e.g., Clarke Error Grid Analysis, sensitivity and specificity in different moments in the day).
To this purpose, members of the ABSPIE Lab are currently involved to collect data and validate the AI model. Data will be collected from the current observational study for the Campania Salute Network (CSN) that is an open registry collecting information from general practitioners and community hospitals in the 5 health districts of the Campania Region, in Southern Italy.
- Porumb, M., Stranges, S., Pescapè, A., Pecchia L. Precision Medicine and Artificial Intelligence: A Pilot Study on Deep Learning for Hypoglycemic Events Detection based on ECG. Sci Rep 10, 170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56927-5Link opens in a new window
- Haleem, M. S., Castaldo, R., Andellini, M., Cisuelo, O., Hattersley, J., & Pecchia, L. (2022). Estimation of ECG Parameters via Deep Learning based ECG Segmentation Tool for Non-invasive Detection of Glycaemic Events.
- Cisuelo, O., Haleem, M. S., Hattersley, J., & Pecchia, L. (2023, September). Spectrogram-Driven Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Non-invasive Hyperglycaemia Detection in Paediatric Type-1 Diabetes via Wearable Sensors. In Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing (pp. 376-386). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- Haleem, M. S., Cisuelo, O., Andellini, M., Castaldo, R., Angelini, M., Ritrovato, M., ... & Pecchia, L. (2024). A Self-Attention Deep Neural Network Regressor for real-time blood glucose estimation in paediatric population using physiological signals. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 92, 106065.
To be populated
