Karuna Sampath
 Research in the Sampath Laboratory focuses on fundamental mechanisms that control development and differentiation of embryonic progenitors and adult stem cells, and the molecular mechanisms underlying these processes using the animal model of human development and disease, zebrafish, and adult human stem cells as experimental systems.
Research in the Sampath Laboratory focuses on fundamental mechanisms that control development and differentiation of embryonic progenitors and adult stem cells, and the molecular mechanisms underlying these processes using the animal model of human development and disease, zebrafish, and adult human stem cells as experimental systems.
We use molecular genetic, genomic, live imaging, proteomic, and embryological approaches to determine the roles of non-coding and coding RNAs, and regulation of nodal signaling.
Our current work focuses on the following themes:
1) Maternal Nodal and Regulation of Nodal signaling
2) Mechanism of maternal nodal RNA as a paradigm for RNAs with both coding and non-coding functions (cncRNAs)
3) Regulation of development by RNA control elements and RBPs (RNA regulons)
4) Microtubule-based RNA transport and localization.
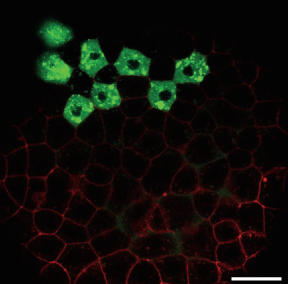
Image shows cells in a 30% epiboly stage zebrafish embryo expressing GFP-tagged Nodal ligand (green) and mCherry tagged Acvr2 receptor (red); scale bar 50 mm.
Selected publications:
- Zaucker, A., Mitchell, C.A., Coker, H.L. and Sampath, K., 2021. Tools to Image Germplasm Dynamics During Early Zebrafish Development. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, p.2231. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.712503
- Zaucker, A., Kumari, P. and Sampath, K., 2020. Zebrafish embryogenesis–A framework to study regulatory RNA elements in development and disease. Developmental biology, 457(2), pp.172-180. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.01.008
- Yi, X., Yu, J., Ma, C., Dong, G., Shi, W., Li, H., Li, L., Luo, L., Sampath, K., Ruan, H. and Huang, H., 2019. The effector of Hippo signaling, Taz, is required for formation of the micropyle and fertilization in zebrafish. PLoS Genetics, 15(1), p.e1007408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007408
- Zaucker, A., Nagorska, A., Kumari, P., Hecker, N., Wang, Y., Huang, S., Cooper, L., Sivashanmugam, L., VijayKumar, S., Brosens, J. and Gorodkin, J., 2018. Translational co-regulation of a ligand and inhibitor by a conserved RNA element. Nucleic acids research, 46(1), pp.104-119. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx938
- Wang, Y., Wang, X., Wohland, T. and Sampath, K., 2016. Extracellular interactions and ligand degradation shape the nodal morphogen gradient. Elife, 5, p.e13879. doi: 10.7554/eLife.13879

