Publications
A complete up-to-date list of publications of Robert can be found on Google Scholar and full-texts might be available from the Warwick Research Active Portal (WRAP).
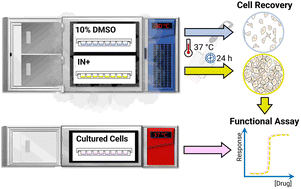
How to unfreeze liver cells without killing them (just to later kill them with drugs)?
This is a real issue in drug screening, especially high throughput assays are suffering from low viability after thawing of cells, and associate labour-intensive remidies. To address this, we helped the Gibson Group to show off their impressive anti-freeze technique in a paper entitled: "Cryopreservation of Assay-Ready Hepatocyte Monolayers by Chemically-Induced Ice Nucleation: Preservation of Hepatic Function and Hepatotoxicity Screening Capabilities"
Being able to recover many HepG2 cells as well as primary hepotocytes as we demonstrate in this paper is a step in the direction to make this process more efficient and reducing variation!
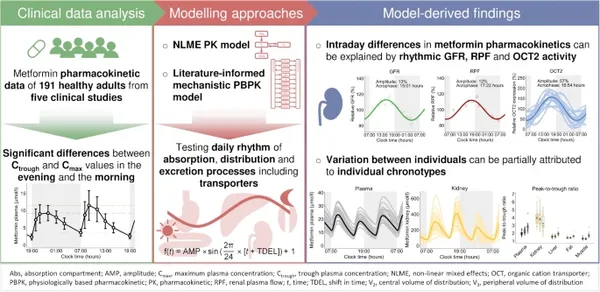
Metformin pharmacokinetics are modulated by the patients indiviual chronotype
Treatment at the optimal time-of-day shows benefits for patients in various indications from cancer to diabetes mellitus, although for example in type 2 diabetes this has not been investigated in dedicated clinical trials. Here, we use a modelling approach to ask if metformin pharmacokinetics exhibit significant variation depending on time of application, and then predict and test what the underlying causes might be.
Analysis of clinical data from a large dataset revealed significant intraday variation of metformin pharmacokinetics. Empirical and mechanistic pharmacokinetic modelling showed that variation in pharmacokinetics could be attributed to rhythms in glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow and organic cation transporter 2 activity. Also, and importantly, interindividual variation was partly explained by individual “chronotype”. This suggests that not only do metformin pharmacokinetics show pronounced time-of-day dependent differences, but also interindividual variability based on chronotype might impact metformin efficacy and present opportunities for future optimised chronomodulated therapy of type 2 diabetes patients.
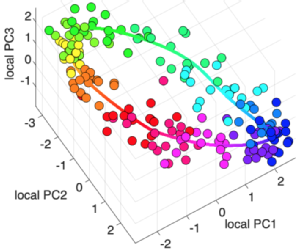
TimeTeller: a tool to probe the circadian clock as a multigene dynamical system
|
|
Great collaboration started by David Rand and Francis Lévi with contributions from many including MRC DTP PhD students Laura Usselmann and Vadim Vasilyev, we describe a novel tool to interrogate the circadian clock from a single sample's transcriptome. We show in many examples how this can deliver useful information not only on the phase of the biological clock in the sample, but also give an estimate on the functionality of the clock. Furthermore, we show how this has potential as a biomarker to stratify data-sets from human tissues as well as inform research in experimental models. The TimeTeller algorithm will be available for use to any interested colleague soon. |
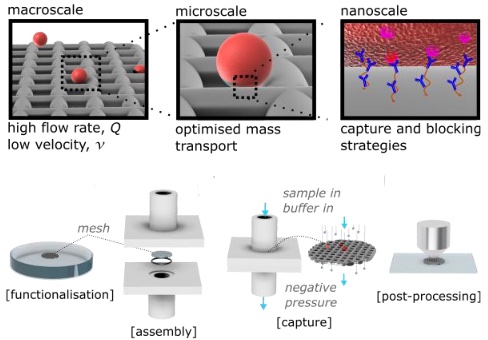
Flow Rate Independent Multiscale Liquid Biopsy for Precision Oncology
Previously as a preprint (arXiveLink opens in a new window), now peer-reviewed out in ACS Sensors. A collaboration led bt Jérôme Charmet and Holosensor Medical Technology Ltd. introducing a new flow rate independent way to trap and then process circulating tumour cells. One stop shop from engineering of the device including simulating the flow conditions to making and testing as proof of principle and then application in a clinical data-set.
Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption alters the lung transcriptome to predispose to viral infection - in mice
Previously a preprint hereLink opens in a new window, now out in iScience:
Great collaboration with Aarti Jagannath's lab in Oxford.
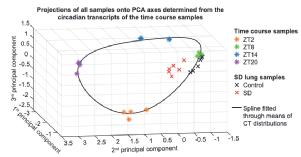 |
Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption (SCRD), as encountered during shift work, increases the risk of respiratory viral infection including SARS-CoV-2. However, the mechanism(s) underpinning higher rates of respiratory viral infection following SCRD remain poorly characterised. To address this, we investigated the effects of acute sleep deprivation on the mouse lung transcriptome. Here we show that sleep deprivation profoundly alters the transcriptional landscape of the lung, causing the suppression of both innate and adaptive immune systems, disrupting the circadian clock, and activating genes implicated in SARS-CoV-2 replication, thereby generating a lung environment that promotes viral infection and associated disease pathogenesis. Our study provides a mechanistic explanation of how SCRD increases the risk of respiratory viral infections including SARS-CoV-2 and highlights therapeutic avenues for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. |