Ultrafast & Terahertz Photonics: Publications
Filter by PI:
Filter by topic:
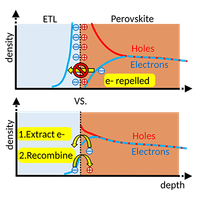
Distinguishing carrier transport and interfacial recombination at perovskite/transport-layer interfaces using ultrafast spectroscopy and numerical simulation
E. Butler-Caddle, K.D.G.I. Jayawardena, A. Wijesekara, R.L. Milot and J. Lloyd-Hughes
Phys. Rev. Applied 22 024103 (Aug 2024)
Temperature-Dependent Structural and Optoelectronic Properties of the Layered Perovskite 2-Thiophenemethylammonium Lead Iodide
Justas Deveikis, Marcin Giza, David Walker, Jie Liu, Claire Wilson, Nathaniel P. Gallop, Pablo Docampo, James Lloyd-Hughes and Rebecca L. Milot
J. Phys. Chem. C , (July 2024)
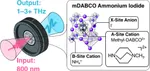
Terahertz Emission via Optical Rectification in a Metal-Free Perovskite Crystal
Nathaniel P. Gallop, Dumitru Sirbu, David Walker, James Lloyd-Hughes, Pablo Docampo and Rebecca L. Milot
ACS Photonics 10 4022 (October 2023)
High-bandwidth perovskite photonic sources on silicon
A. Ren, H. Wang, L. Dai, J. Xia, E. Butler-Caddle, J.A. Smith, ... S.A. Hindmarsh, A.M. Sanchez, J. Lloyd-Hughes, S. J Sweeney, ... and Wei Zhang
Nature Photonics 17, 798–805 (July 2023)
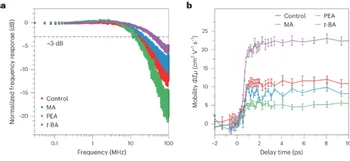
Resolving the Ultrafast Charge Carrier Dynamics of 2D and 3D Domains within a Mixed 2D/3D Lead-Tin Perovskite
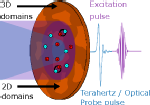
Jake D. Hutchinson, Edoardo Ruggeri, Jack M. Woolley, Géraud Delport, Samuel D. Stranks, Rebecca L. Milot
Advanced Functional Materials 2305736, (August 2023)
Terahertz photoconductance dynamics of semiconductors from sub-nanosecond to millisecond timescales
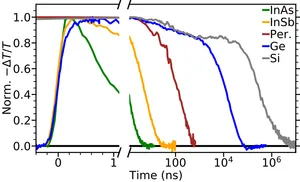
E. Butler-Caddle, N.E. Grant, S.L. Pain, J.D. Murphy, K.D.G.I. Jayawardena and J. Lloyd-Hughes
Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 012101 (Jan 2023)
Predicting Solar Cell Performance from Terahertz and Microwave Spectroscopy
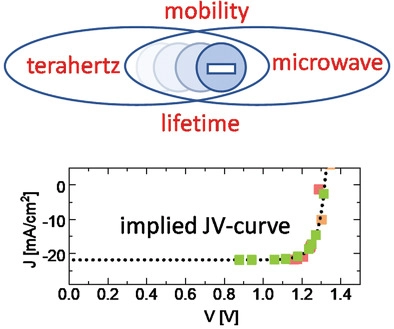
H. Hempel, T.J. Savenjie, M. Stolterfoht, J. Neu, M. Failla, V.C. Paingad, P. Kužel, E.J. Heilweil, J.A. Spies, M. Schleuning, J. Zhao, D. Friedrich, K. Schwarzburg, L.D.A. Siebbeles, P. Dörflinger, V. Dyakonov, R. Katoh, M.J. Hong, J.G. Labram, M. Monti, E. Butler-Caddle, J. Lloyd-Hughes, M.M. Taheri, J.B. Baxter, T.J. Magnanelli, S. Luo, J.M. Cardon, S. Ardo, T. Unold
Advanced Energy Materials 2102776 (Feb 2022)
The 2021 ultrafast spectroscopic probes of condensed matter roadmap
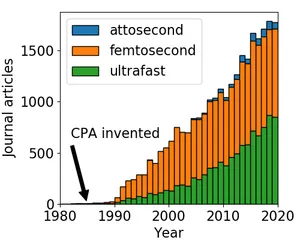
J. Lloyd-Hughes, P.M. Oppeneer, T. Pereira dos Santos, A. Schleife, S. Meng, M.A. Sentef, M. Ruggenthaler, A. Rubio, I. Radu, M. Murnane, X. Shi, H. Kapteyn, B. Stadtmüller, K.M. Dani, F.H. da Jornada, E. Prinz, M. Aeschlimann, R.L. Milot, M. Burdanova, J. Boland, T. Cocker and F. Hegmann
J. Phys.: Cond. Matt. 33 353001 (July 2021)
Layered Perovskites in Solar Cells: Structure, Optoelectronic Properties, and Device Design
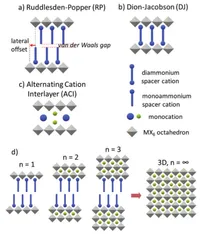
D. Sirbu, F. H. Balogun, R. L. Milot and P. Docampo
Advanced Energy Materials (May 2021)
Nanotechnology for catalysis and solar energy conversion
U. Banin, N. Waiskopf, L. Hammarström, G. Boschloo, M. Freitag, E.M.J. Johansson, J. Sá, H. Tian, M.B. Johnston, L.M. Herz
Metal composition influences optoelectronic quality in mixed-metal lead-tin triiodide perovskite solar absorbers
M. T. Klug, R. L. Milot, J.B. Patel, T. Green, H. C. Sansom, M. D. Farrar, A. J. Ramadan, S. Martani, Z. Wang, B. Wenger, J. M. Ball, L. Langshaw, A. Petrozza, M. B. Johnston, L. M. Herz and H. J. Snaith
Energy & Environmental Science (May 2020)
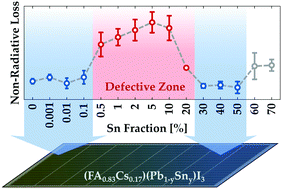
Approaching the Shockley-Queisser limit for fill factors in lead–tin mixed perovskite photovoltaics
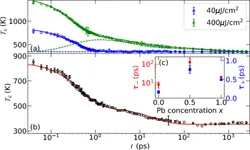
K.D.G.I. Jayawardena, R.M.I. Bandara, M. Monti, E. Butler-Caddle, T. Pichler, H. Shiozawa, Z. Wang, S. Jenatsch, S.J. Hinder, M.G. Masteghin, M. Patel, H.M. Thirimanne, W. Zhang, R.A. Sporea, J. Lloyd-Hughes and S. R. P. Silva
J. Mater. Chem. A 8 693 (Jan 2020) [ pdf ] [ ref ]
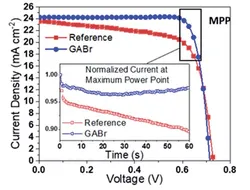 The performance of all solar cells is dictated by charge recombination. A closer to ideal recombination dynamics results in improved performances, with fill factors approaching the limits based on Shockley-Queisser analysis. It is well known that for emerging solar materials such as perovskites, there are several challenges that need to be overcome to achieve high fill factors, particularly for large area lead-tin mixed perovskite solar cells. Here we demonstrate a strategy towards achieving fill factors above 80% through post-treatment of a lead-tin mixed perovskite absorber with guanidinium bromide for devices with an active area of 0.43 cm2. This bromide post-treatment results in a more favourable band alignment at the anode and cathode interfaces, enabling better bipolar extraction. The resulting devices demonstrate an exceptional fill factor of 83%, approaching the Shockley–Queisser limit, resulting in a power conversion efficiency of 14.4% for large area devices.
The performance of all solar cells is dictated by charge recombination. A closer to ideal recombination dynamics results in improved performances, with fill factors approaching the limits based on Shockley-Queisser analysis. It is well known that for emerging solar materials such as perovskites, there are several challenges that need to be overcome to achieve high fill factors, particularly for large area lead-tin mixed perovskite solar cells. Here we demonstrate a strategy towards achieving fill factors above 80% through post-treatment of a lead-tin mixed perovskite absorber with guanidinium bromide for devices with an active area of 0.43 cm2. This bromide post-treatment results in a more favourable band alignment at the anode and cathode interfaces, enabling better bipolar extraction. The resulting devices demonstrate an exceptional fill factor of 83%, approaching the Shockley–Queisser limit, resulting in a power conversion efficiency of 14.4% for large area devices.
The Effects of Doping Density and Temperature on the Optoelectronic Properties of Formamidinium Tin Triiodide Thin Films
R. L. Milot, M. T. Klug, C. L. Davies, Z. Wang, H. Kraus, H. J. Snaith, M. B. Johnston, and L. M. Herz
Advanced Materials (Sept 2018) [ pdf ] [ ref ]
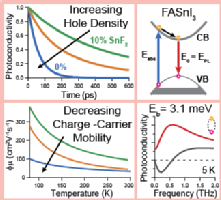 Optoelectronic properties are unraveled for formamidinium tin triiodide (FASnI3) thin films, whose background hole doping density is varied through SnF2 addition during film fabrication. Monomolecular charge‐carrier recombination exhibits both a dopant‐mediated part that grows linearly with hole doping density and remnant contributions that remain under tin‐enriched processing conditions. At hole densities near 1020 cm−3, a strong Burstein–Moss effect increases absorption onset energies by ≈300 meV beyond the bandgap energy of undoped FASnI3 (shown to be 1.2 eV at 5 K and 1.35 eV at room temperature). At very high doping densities (1020 cm−3), temperature‐dependent measurements indicate that the effective charge‐carrier mobility is suppressed through scattering with ionized dopants. Once the background hole concentration is nearer 1019 cm−3 and below, the charge‐carrier mobility increases with decreasing temperature according to ≈T−1.2, suggesting that it is limited mostly by intrinsic interactions with lattice vibrations. For the lowest doping concentration of 7.2 × 1018 cm−3, charge‐carrier mobilities reach a value of 67 cm2 V−1 s−1 at room temperature and 470 cm2 V−1 s−1 at 50 K. Intraexcitonic transitions observed in the THz‐frequency photoconductivity spectra at 5 K reveal an exciton binding energy of only 3.1 meV for FASnI3, in agreement with the low bandgap energy exhibited by this perovskite.
Optoelectronic properties are unraveled for formamidinium tin triiodide (FASnI3) thin films, whose background hole doping density is varied through SnF2 addition during film fabrication. Monomolecular charge‐carrier recombination exhibits both a dopant‐mediated part that grows linearly with hole doping density and remnant contributions that remain under tin‐enriched processing conditions. At hole densities near 1020 cm−3, a strong Burstein–Moss effect increases absorption onset energies by ≈300 meV beyond the bandgap energy of undoped FASnI3 (shown to be 1.2 eV at 5 K and 1.35 eV at room temperature). At very high doping densities (1020 cm−3), temperature‐dependent measurements indicate that the effective charge‐carrier mobility is suppressed through scattering with ionized dopants. Once the background hole concentration is nearer 1019 cm−3 and below, the charge‐carrier mobility increases with decreasing temperature according to ≈T−1.2, suggesting that it is limited mostly by intrinsic interactions with lattice vibrations. For the lowest doping concentration of 7.2 × 1018 cm−3, charge‐carrier mobilities reach a value of 67 cm2 V−1 s−1 at room temperature and 470 cm2 V−1 s−1 at 50 K. Intraexcitonic transitions observed in the THz‐frequency photoconductivity spectra at 5 K reveal an exciton binding energy of only 3.1 meV for FASnI3, in agreement with the low bandgap energy exhibited by this perovskite.
Efficient Intraband Hot Carrier Relaxation in the Perovskite Semiconductor Cs1-xRbxSnI3 Mediated by Strong Electron-Phonon Coupling
M. Monti, S. Tao, M. Staniforth, A. Crocker, E. Griffin, A. Wijesekara, R.A. Hatton, and J. Lloyd-Hughes
J. Phys. Chem. C 122 20669 (Aug 2018) [ pdf ] [ ref ]
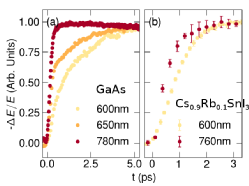 The dynamic increase in THz photoconductivity resulting from energetic intraband relaxation was used to track the formation of highly mobile charges in thin films of the tin iodide perovskite Cs1-xRbxSnI3, with x=0 and x=0.1. Energy relaxation times were found to be around 500fs, comparable to those in the prototypical inorganic semiconductor GaAs. At low excess energies the efficient intraband energy relaxation in the lowest conduction and valence bands of Cs1-xRbxSnI3 can be understood within the context of the Fröhlich electron-phonon interaction, with a strong coupling strength. For higher excess energies the photoconductivity rise time lengthens in accordance with carrier injection into multiple bands, identified by quantitative first-principles bandstructure calculations and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The findings contribute to the development of design rules for photovoltaic devices capable of extracting hot carriers from perovskite semiconductors.
The dynamic increase in THz photoconductivity resulting from energetic intraband relaxation was used to track the formation of highly mobile charges in thin films of the tin iodide perovskite Cs1-xRbxSnI3, with x=0 and x=0.1. Energy relaxation times were found to be around 500fs, comparable to those in the prototypical inorganic semiconductor GaAs. At low excess energies the efficient intraband energy relaxation in the lowest conduction and valence bands of Cs1-xRbxSnI3 can be understood within the context of the Fröhlich electron-phonon interaction, with a strong coupling strength. For higher excess energies the photoconductivity rise time lengthens in accordance with carrier injection into multiple bands, identified by quantitative first-principles bandstructure calculations and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The findings contribute to the development of design rules for photovoltaic devices capable of extracting hot carriers from perovskite semiconductors.
Highly Sensitive Terahertz Thin-Film Total Internal Reflection Spectroscopy Reveals in Situ Photoinduced Structural Changes in Methylammonium Lead Halide Perovskites
Q. Sun, X. Liu, J. Cao, R.I. Stantchev, Y. Zhou, X. Chen, E.P.J. Parrott, J. Lloyd-Hughes, N. Zhao, and E. Pickwell-MacPherson
J. Phys. Chem. C 122 17552 (June 2018) [ pdf ] [ ref ]
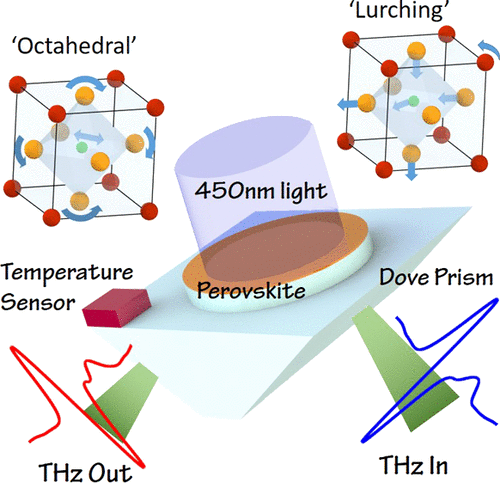
Terahertz (THz) thin-film total internal reflection (TF-TIR) spectroscopy is shown to have an enhanced sensitivity to the vibrational properties of thin films in comparison with standard THz transmission spectroscopy. This increased sensitivity was used to track photoinduced modifications to the structure of thin films of methylammonium (MA) lead halide, MAPbI3–xBrx (x = 0, 0.5, 1, and 3). Initially, illumination strengthened the phonon modes around 2 THz, associated with Pb–I stretch modes coupled to the MA ions, whereas the 1 THz twist modes of the inorganic octahedra did not alter in strength. Under longer term illumination, the 1 THz phonon modes of encapsulated films slowly reduced in strength, whereas in films exposed to moisture and oxygen, these phonons weaken more rapidly and blue-shift in frequency. The rapid monitoring of environmentally induced changes to the vibrational modes afforded by TF-TIR spectroscopy offers applications in the characterization and quality control of the perovskite thin-film solar cells and other thin-film semiconductors.
Cs1−xRbxSnI3 light harvesting semiconductors for perovskite photovoltaics
K.P. Marshall, S. Tao, M. Walker, D.S. Cook, J. Lloyd-Hughes, S. Varagnolo, A. Wijesekara, D. Walker, R.I. Walton and R.A. Hatton
Materials Chemistry Frontiers 2:1515 (June 2018) [ pdf ] [ ref ]
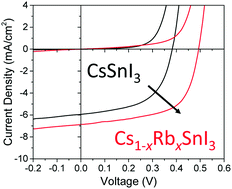
We show that films of the 3-dimensional perovskite Cs1−xRbxSnI3 can be prepared from room temperature N,N-dimethylformamide solutions of RbI, CsI and SnCl2 for x ≤ 0.5, and that for x ≤ 0.2 film stability is sufficient for utility as the light harvesting layer in inverted photovoltaic (PV) devices. Electronic absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy measurements supported by computational simulation, show that increasing x increases the band gap, due to distortion of the lattice of SnI6 octahedra that occurs when Cs is substituted with Rb, although it also reduces the stability towards decomposition. When Cs0.8Rb0.2SnI3 perovskite is incorporated into the model inverted PV device structure; ITO|perovskite|C60|bathocuproine|Al, an ∼120 mV increase in open-circuit is achieved which is shown to correlate with an increase in perovskite ionisation potential. However, for this low Rb loading the increase in band gap is very small (∼30 meV) and so a significant increase in open circuit-voltage is achieved without reducing the range of wavelengths over which the perovskite can harvest light. The experimental findings presented are shown to agree well with the predictions of density functional theory (DFT) simulations of the stability and electronic structure, also performed as part of this study.