Migrants in Devon
Inter-parish, transhumant and transient migrants in Devon: 1600-1800
Marion Hardy
Devon History Society & British Association for Local History
John Milford was born in Chulmleigh in Devon, marked ‘C’ in Figure 1, about 1725/6, the base child of Sarah Milford. He became a parish apprentice until he was 17, when his master had no further employment for him. He found residential employment at a weekly rate of 6d until he was 19 when he went to Newton Bushell (Newton Abbot) for 6 months before gaining a contract to go to Newfoundland for ‘about a year’, so probably for two summers and a winter. He returned to Bristol, worked by the week for some time and then spent a year as a labourer on the Bridgewater and Wells turnpike road. John then returned to work in Rose Ash in Devon. When he was turned away he became a day labourer and married about 5 years later. In 1766, he was examined by the overseers of Chulmleigh. John had moved between parishes, he had undertaken transatlantic transhumance in the fishing industry and then been a transient migrant through Somerset to arrive back in Chulmleigh the overseers’ settlement examination revealed his story.
Information from settlement certificates and settlement examinations is available after 1662, but other information is available from the records of churchwardens and Devon county quarter sessions’ record books and bundles of examinations. (The relative importance of these records changed in 1700. )
Inter-parish migration was probably the most common form of population movement, although the evidence before 1662 is limited to that from churchwardens’ accounts and quarter sessions’ records. Inter-parish movements were initially usually voluntary and settlement certificates were intended to facilitate such movements.
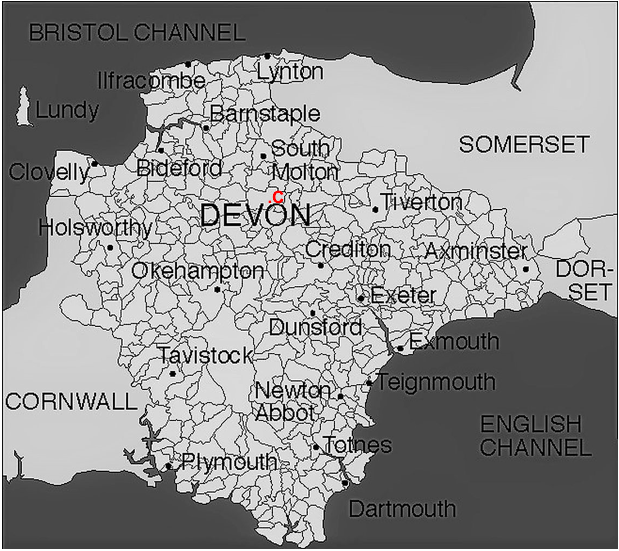
Figure 1: Historic Parishes of Devon. Map created using: www.genuki.org.uk
John Bulley, a tailor, his wife and child, with a settlement certificate from the parish of Ipplepen, arrived in nearby Combeinteignhead in 1722, but 26 inhabitants of the parish petitioned against them as the family was thought to be trying to gain a settlement in the parish. Ipplepen would have had to resume responsibility for the family. The outcome is not known, but in law, the Bulleys could not be removed unless they became chargeable. However, other parishes, like South Molton, for which there are ninety-one settlement certificates dated from 1652 to 1783, were evidently more welcoming. Our John was examined to establish whether or not Chulmleigh was his parish of legal settlement. A parish was responsible for the cost of a person’s removal home. In 1760/1, South Molton gave J. Kemp’s widow 8s to help her get to Launceston in Cornwall; John Avery, who was going only to Bideford, received 1s.
A settlement decision might be disputed by the other parish, in which case, the dispute was taken to the quarter sessions for resolution. For the disputing parishes of Devon, from 1750 to 1769 inclusively, the distances between them range from the neighbouring parish to out of county into Cornwall, Somerset and as far as Gloucester. Some of those examined in Barnstaple from 1783 to 1799 might travel even further. In April 1783, John Berry said that he was born in Little Dunkeld, Perthsire and enlisted in the 77th Regiment of Foot (Highlanders), from which he had been discharged. He had married Sarah Davies, daughter of a Barnstaple widow, in Kingsclere, Hants, in January. They were probably sent to Scotland. Marriage to a soldier, to a lesser extent a seaman, might lead to long migration distances for wives as a wife’s legal parish was that of her husband.
Sometimes one feels that the migrants became the victims of officialdom. The woman and her son destined for ‘East Buckley’ were sent back to Lancashire as Devon does not have such a place—but it does have East Budleigh? When a child is affected it seems worse. Six year old Martha had to be left temporarily in Devon to be later conveyed workhouse to workhouse back to Prestbury, Cheshire as her name had been omitted from the paper work for the mother and children.
The more usual distances for such inter-parish movements show a general decline with distance, but Barnstaple and Combeinteignhead are notably different: Barnstaple has a marked increase for over 30 miles, which is primarily the influence of the proportion of soldiers in the sample; that for Combeinteignhead is surprisingly even across the distances. Combeinteignhead is adjacent to Newton Bushell, which was the recruitment centre for the likes of John Milford for the transhumant Newfoundland fishing trade. A number of the merchants lived near the Teign estuary. Many a parish apprentice went to Newfoundland on a contract as a next stage of life. It was said that every labouring man of Coffinswell (adjacent to Combeinteignhead) had been to Newfoundland. Nor did the person have to be familiar with the sea, as every fifth man recruited should be a ‘green man’, i.e. from the land.
Figure 2 shows that a number of migrants, like John, moved towards the Newfoundland contract in stages and not all returned directly to their home parishes. For many, one such contract was sufficient, but for others an annual migration became the norm: out in March/April, working in actual fishing or fish curing ashore for the summer and returning each October, or later if via the West Indies or an Iberian or Mediterranean port, to spend the winter as a labourer or working at any skill, such as blacksmithing, carpentry or coopering. Richard Beer, born in Netherexe but apprenticed to Kenton, went to sea at age 14 or 15 and made seven voyages to Newfoundland and then was pressed into the navy for eight or more years, before he was discharged when he went to Chudleigh where he worked and married. John Peppell of Kingsbrinton (Brompton Regis) Somerset, moved to Bickleigh for six months and then went to Stokeinteignhead from which he spent nine years making annual voyages before going to Widecombe in the Moor for fifteen years and then to Combeinteignhead where he lived in a cottage in the right of his wife.
Those who were part of a share system might save enough to own a small fishing boat which could be kept in Newfoundland and then travel out and back each year. By 1816/17, Robert Tolchard (Tolcherd) had been making fishing trips for nearly 50 years. When he died in East Ogwell, near Newton Abbot, in 1825, he left his property in Torbay, Newfoundland, to his daughters. Robert was fortunate, as there were hazards, ranging from the weather at sea to being taken as a slave by Barbary pirates or captured by the French.
John Samson was on his second transatlantic migration when he was taken captive by the French and involuntarily spent four months in France. He returned to Bovey Tracey and became a potter.
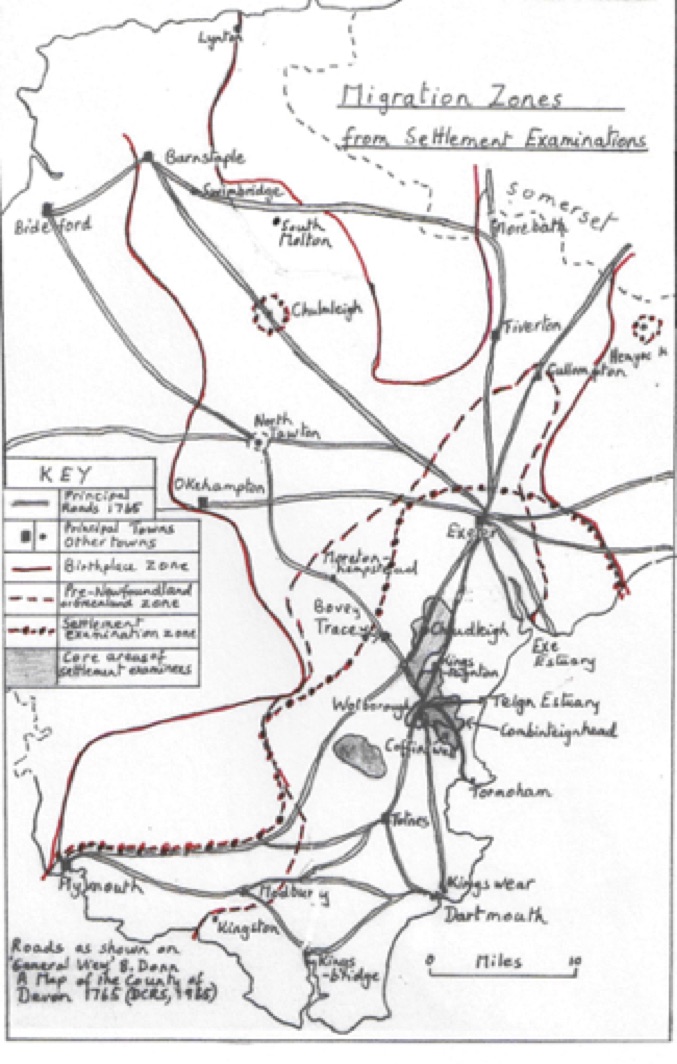
Figure 2: Transhumant migrants who left for Newfoundland from South Devon
Edward Tree went to Newfoundland each year and spent the winters with a widowed landlady, Susanna Boyes, in Paignton. The relationship ‘developed’ and the following spring Edward and then pregnant Susanna went out to Newfoundland among about 200 passengers on Captain Bartlett’s ship and settled at Bay Bulls. Seven years later they were living there as man and wife and had three children. Over time, some became temporary or permanent emigrants from Devon.
The last outbound, or the first inbound, port of call for the Newfoundland ships was in southern Ireland. This makes sense geographically, but there was also a social connection since the establishment of the Elizabethan plantations in Munster. Apart from economic migrants, famine in the 1630s gave rise to Irish migrants in Devon as did religious conflict and wars.
In 1644, Elizabeth Butler & her three sonnes received charity on ‘… the Sixth daie of December she being a ministers wife & being robed of all their goods in Ireland xijd’ In 1649, a total of about 90 adult Irish people passed through Tiverton, including a group of 24 who received 7s and 2 Irish women and 7 children who were given 5s.
Many of the Irish were transient migrants as they passed through Devon hoping to reach London: if their migration failed any misdemeanour might result in their free return travel to their port of arrival, which was likely to have been in north Devon or north Cornwall, so a good many found themselves traversing Devon a second time..
Seamen, both merchant and naval, especially from the Low Countries, discharged soldiers and those arriving from overseas were also transient migrants as they returned home from their ports of landing or sought a livelihood in England. Those who were rescued at sea became supernumeraries and were landed at the first port of call. Braunton in particular saw a number of foreign personnel or travellers following a spate of shipwrecks in the 1680s for which the Calendar of Sate Papers provides corroboration. These people also became transient migrants.
Towards the end of the eighteenth century, one finds a considerable number who have been born in Newfoundland or America visiting England. In 1785, Exeter examined vagrant George Martin who had been born in Newfoundland. He was whipped and sent to his father’s legal settlement, Portsmouth, by pass. In making his journey, he became a transient migrant through eastern Devon, Dorset and so to Hampshire. Some were sent back and some just ‘turned loose’ into the county.
Some become almost constantly transient migrants, although it might be related to service in the forces. George Walters was born in Holsworthy and apprenticed in Hatherleigh. He joined a regiment at Sherborne in Dorset and served for eleven or twelve years, before being discharged as ‘incapable’. In Scotland, he had married Elizabeth who had been born at Banff and they had lived together ever since. Their three surviving children had been born one in Scotland, one at sea and Catherine had been born at Redruth, Cornwall. Their return to Devon would have led to his parish of legal settlement.
Unless there were multiple men called Daniel Hunt, he was recorded twelve times as he traversed Devon seven times in the ten years from 1666 to 1676. sometimes said to be travelling to/from Cornwall. Six of the entries are by the churchwardens of South Tawton. Initially the entries seem plausible, but some apparent discrepancies occur. The thirteenth record is of him, with his wife, in the county workhouse at St Thomas, Exeter in 1676, because they had been begging with counterfeit passes. They were to be returned to Sligo in Ireland.
How much had he been getting away with? Not to mention others who contrived to obtain counterfeit passes. Nicholas Frost and his two companions managed to travel from just north of Plymouth, to Witheridge in north Devon where the constable’s suspicions proved justified as they said that they had been cast ashore at Rame Head. The certificate claimed it was at Land’s End. Only Nicholas was a genuine seaman; the other two were land’s men. Roger Camp travelled from Bideford, supposedly, to Exeter, where someone checked on the name of the mayor of Bideford: it wasn’t Davis.
Others lived itinerant lives to gain a livelihood. Thomas Gardner, a saddler of Glastonbury had married Margaret in Salisbury. In the last eight years, she had given birth to their three children, one each in St. Columb (Cornwall), Newton St. Cyres and Kentisbeare, both in Devon, although the first had died at Poughill. He may have been moving for work, successfully up to the time of his examination. Others moved around for work but when work was unavailable were reduced to stealing, with the danger of being caught, or they resorted to begging, like James Gubbins, who told the justice that he was tired of this life.
Churchwardens’ records, suggests that those moving only within Devon in the seventeenth century were a small proportion of the total, perhaps because they seemed to record more details of the unusual. The numbers appear greater when vagrancy and inter-parish disputes are taken into account. For a good many, transhumant migration for the Newfoundland fishery was at least a component of life’s movements. A few of those who travelled in Devon seem to have been permanently itinerant, like Nicholas Reeve of Porlock (Somerset) who told a justice that ‘he dwelte every wheare but especially in every good towne or city wheare there was a Goal or Prison…’ However, the number who became transient migrants through Devon is high and over longer distances than might be expected, often as a result of problems in Ireland, time at sea or wars.
This paper was presented at 'Parishes and Migration', the Sixteenth Warwick Symposium on Parish Research in May 2018.
It is also available in pdf format.
