Dept News
New paper published in Energy & Environmental Science
A new paper has been published in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Energy & Environmental Science by postdoc Yi Yuan, which has been selected as a ‘Research Highlight’ by Nature Energy due to its importance in the field.
The research is part of an ongoing collaboration between University of Warwick, University of Oxford and Central South University China, where they are exploring the potential of a new type of safe and cheap rechargeable battery chemistry that is based on zinc rather than lithium.
A major challenge with this type of new battery chemistry is that the zinc used continually corrodes, causing the battery to lose capacity over time. However, this problem is hidden and so often ignored. Yi Yuan, Alex Robertson and colleagues used a powerful technique at Warwick – in situ transmission electron microscopy – to capture this process as it occurs at the microscale. This allowed Yi to develop a new understanding of the detailed mechanism behind the corrosion, and use this understanding to employ suitable modifications to curtail it.
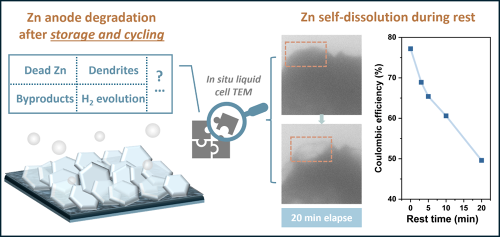
A cartoon (left) showing the problem of zinc undergoing various degradation processes inside a battery. By using in situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Warwick researchers captured a self-dissolution corrosion process (right) as it occurred, which contributed to reducing the battery efficiency.
Energy & Environmental Science is a leading international journal publishing high-impact research at the intersection of energy technology and environmental science, aimed at accelerating the global energy transition. Nature Energy is one of the most influential journals globally in both energy and environmental sciences.
