Question types
With online assessments, you have access to a broader range of question types than traditional paper-based exams, giving you more flexibility to choose the best options for your subject. When used well, this variety can make exams more engaging for students.
In addition to question types, Questionmark Perception offers other valuable features like randomization, branching, and feedback at different levels (question, block, or end-of-assessment) to enhance the assessment experience.
Here’s an overview of the different question types available in Questionmark Perception:
- Drag-and-drop
- Essay question
- Fill-in-the-blank
- Hotspot
- Matching
- Multiple choice
- Multiple response (score per choice)
- Knowledge matrix
- Survey matrix
- Likert scale
- Numeric question
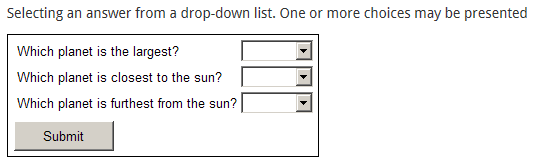
- Pull-down list/drop-down list
- Select-a-blank
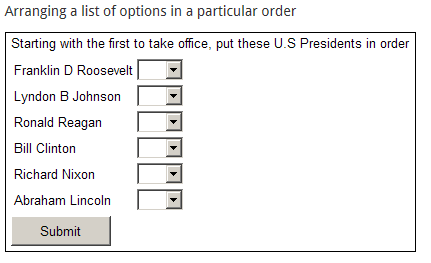
- Rank-in-order
- True/False
- Word response/text match
- Job task analysis
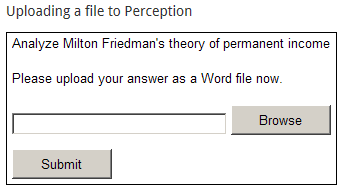
- File upload
- Explanation
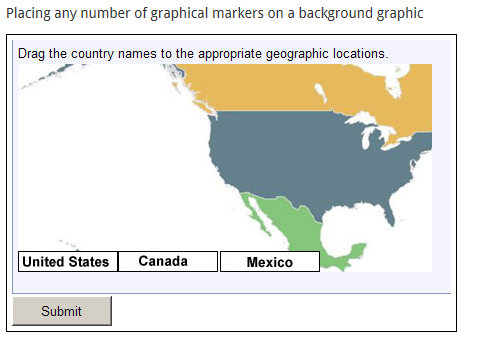
- Drag-and-drop: the participant clicks and drags up to ten images into position. The feedback and score is dependant upon the final position of the images.
- Essay question: the participant answers by typing up to 30,000 characters of text. You may define what is right or wrong in advance by entering a list of acceptable answers or print out a report of the responses for manual grading. The logic can also allow scoring based on the presence or absence of keywords or key phrases. This question type is also used to solicit opinions or suggestions on a particular subject.

- Fill-in-the-blank: the participant is presented with a statement where one or more words are missing and completes the missing words. The score can be determined from checking each blank against a list of acceptable words and can checked for misspelled words.

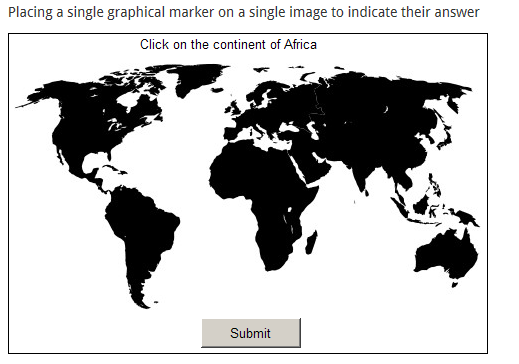
- Hotspot: a participant clicks on a picture to indicate their choice. Depending upon their choice, certain feedback and grades will be assigned. A graphics editor is provided to simplify specifying the choice areas.
- Matching: two series of statements/words are presented and the participant must match items from one list to items within the other list. See how to create one with an example here.
- Multiple choice: the participant selects one choice from up to 40 possible answers. There is no limit to the length of each answer.

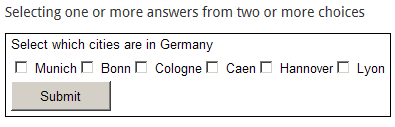
- Multiple response (score per choice): similar to multiple choice except the participant is not limited to choosing one response; he/she can select none, one or more of the choices offered.
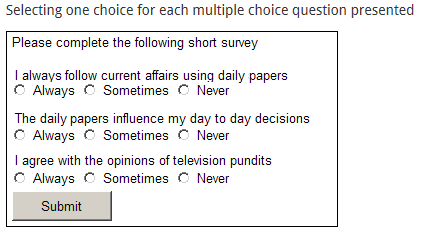
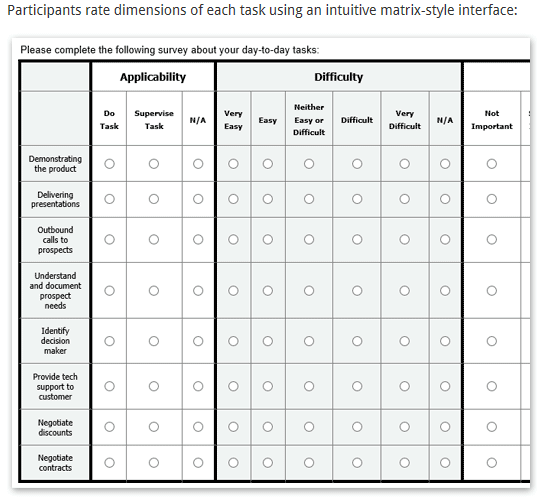
Matrix: this question type presents several multiple-choice questions together where the participant selects one choice for each statement or question presented. This question type is used to cross-relate responses from a single item.
- Knowledge matrix:
- Survey matrix:
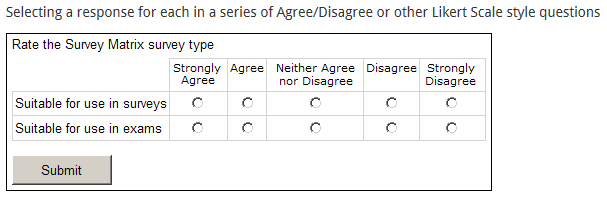
- Likert scale: the participant selects one of several options such as "strongly agree" through "strongly disagree" that are weighted with numbers to aid analysis of the results.

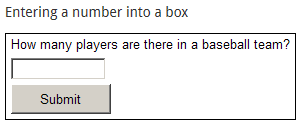
- Numeric questions: a participant is prompted to enter a numeric value, and this may be scored as one value for an exact answer and another score if the response is within a range.
- Pull-Down List (drop-down list): a series of statements are presented and the participant can match these statements with a pull-down list.
- Select-a-blank: the participant is presented with a statement where a word is missing; words can be selected from a pull-down list to indicate their answer.

- Ranking (Rank in Order): a list of choices must be ranked numerically with duplicate matches not allowed.
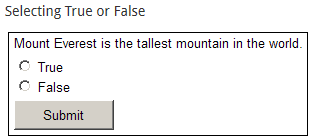
- True/False: the participant selects "true" or "false" in response to the question.
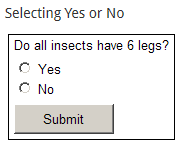
- Yes/No: the participant selects "Yes" or "No" in response to the question.
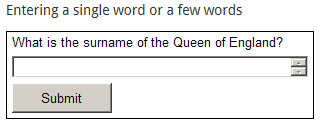
- Word response (text match): the participant types in a single word or a few words to indicate their answer. You define right or wrong words or phrases in advance by entering a list of acceptable answers. The grading logic can also allow scoring based on the presence or absence of keywords or key phrases and check for misspellings.
- Job task analysis: suitable for individual assessments where students have to demonstrate that they master a perform a certain task, follow a procedure, negotiation/discussion etc. The form is filled in by the teacher to capture performance.
- File upload:
- Explanation: insert text or graphics for the participant to view prior to answering a series of questions (instructions, background information etc.).

