From authoring to reporting - the eAssessment lifecycle
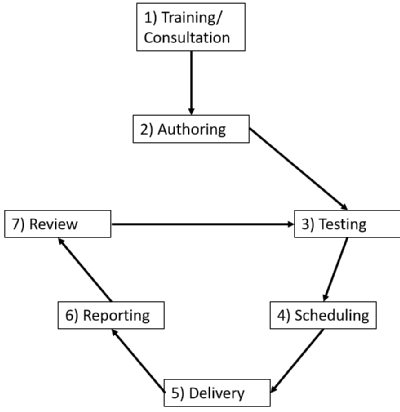
Step 1 - Training/Consultation:
It is advisable to undertake a short training or consultation session where you can familiarise yourself with all functionalities of Questionmark Perception. Look for courses or register interest here. We can show you what is possible and how your colleagues are making best use of QM Perception.
Step 2 - Authoring:
- Prepare your assessment while considering the functionalities of QM Perception to make the best use of the software.
- Create assessment in QM Perception or send it to the eAssessment Team to do it for you.
Step 3 - Testing:
Test assessment whether it works properly:
- Are you happy with the layout/design?
- Are you using the accessibility functions?
- Do you need a special character palette?
- Is the scoring correct?
- Is the feedback correct?
- Are there alternative answers that are correct as well?
- Is the time setting correct?
Step 4 - Scheduling:
Let the eAssessment Team know about scheduling:
- When will this assessment be delivered: day and time?
- Is it an exam or a self-assessment?
- Who will be taking the exam?
- Are there students who have an extended exam time?
- Is there a time limit to take the exam or self-assessment?
- How many attempts should students get?
- Which room have you booked for the exam?
- Do you need headphones or other equipment?
Step 5 - Delivery:
At least one member of the eAssessment team will be joining you for exams if required and will bring equipment along. We can help to make sure all students are taking the exam under secure browser conditions and help out with other technical issues.
Alternatively, an assessment can be set up to be accessed via an open link. This is suitable for when you don’t know who will be taking the assessment in advance.
Step 6 - Reporting:
QM Perception users with admin rights on the assessment can pull the results and create reports as soon as the students have finalised the assessment. Reporting functionalities include:
- Demographics filter
- Question item performance analysis
- User grouping to compare different sets of students
- Breakdown of results by assessment, topic or item
The results can be downloaded in HTML, PDF or CSV.
Have a look at the analytics features in this short video!
Step 7 – Review:
Revise the questions and assessment critically and amend accordingly:
- Have a close look at questions with a particularly high and particularly low item level performance: Where they too hard/easy? Could there be a misunderstanding? Could there be alternative correct answers?
- Did students complain about a certain question or aspect of the assessment? Is the complaint justified? How could it be resolved? (No need to necessarily give in.)
- Will you change the content of the lecture? Change the questions accordingly.
- Are there new features in QM Perception which you can make use of?
- Has the course literature changed to which you make reference in the feedback? Please change the feedback accordingly.
Contents
- Introduction to eStream
- Access your eStream content
- Uploading videos to eStream
- Edit videos in eStream
- Edit video thumbnail
- Uploading a closed captions (subtitles) file to eStream
- Add eStream videos to Mahara
- Sharing eStream videos to Moodle
- Sharing an eStream video with a link
- Setup a video assignment in Moodle
